AI for Clinical Success
Evergreen Therapeutics leverages AI technology to integrate multi-omics, clinical, and real-world data, thereby enhancing the quality of scientific design from the inception of drug development. The company has innovatively developed three core technological components: a cross-species translational prediction tool, a mechanism prioritization system, and a target-population-disease mapping framework. These components address long-standing challenges in the clinical development phase, significantly improving the success rate of drug candidates entering clinical trials, effectively reducing R&D costs, and shortening development cycles. Its proprietary pipelines have successfully utilized these technological advancements, receiving practical validation and recognition from the FDA. This marks a pivotal shift in new drug development, moving from traditional “probabilistic trial-and-error” approaches towards a data-driven, scientifically designed model with a higher probability of success.
Our Approach
EG-501
80%
NPSLE-CI affects up to 80% of SLE patients.
EG-501 is an investigational small molecule oral tablet targeting Cognitive Impairment (CI) in Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (NPSLE).
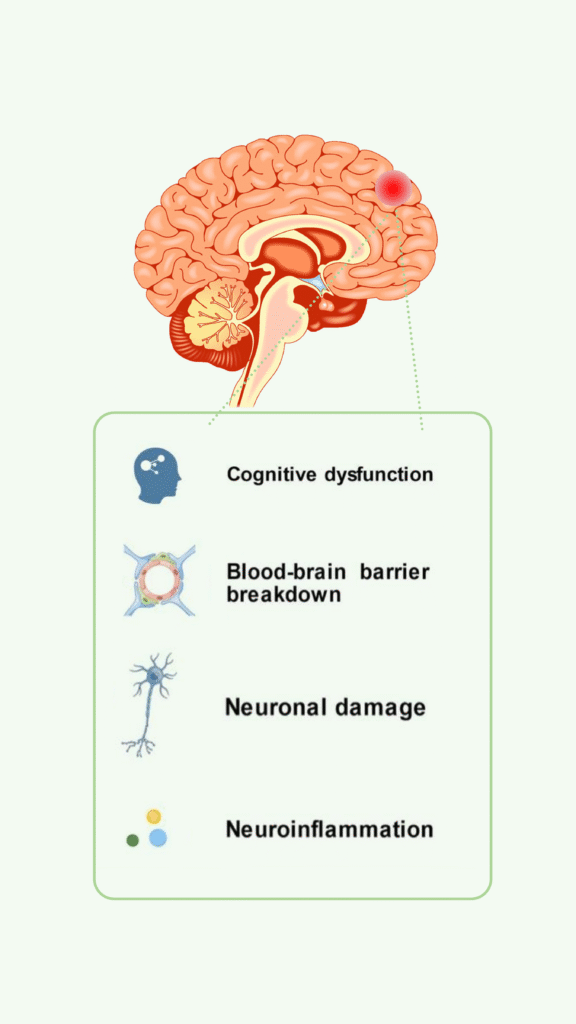
Disease Background
- High Prevalence Rate and Core Symptoms: Cognitive impairment in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE-CI) is a serious manifestation of SLE. It leading to irreversible disability, high mortality (SMR 2-14x), and substantial socioeconomic burden ($10,000-$50,000 annual direct costs per patient; ~65% work disability).
Unmet Medical Needs
- Currently, there are no therapies targeting its core excitotoxic/neuroinflammatory mechanisms, and current symptomatic management is ineffective—resulting in a substantial unmet medical need.
EG-501’s Mechanism of Action
- In NPSLE, acute flares elevate glutamate via cytokine-mediated BBB permeability and microglial NO production, leading to excitotoxic synaptic overload and reversible cognitive symptoms (e.g., impaired processing speed, attention).
- EG501 is a low-affinity, non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist that selectively blocks pathologic glutamate excitotoxicity, BBB compromise, and microglial activation in NPSLE—while preserving physiologic synaptic signaling for learning/memory.
- EG501 provides dual-phase benefit:acute restoration from reversible dysfunction + chronic neuroprotection
AI platform
60%
AI Platform Reduces Innovative Drug Development Costs by >60%
The AI platform plays a pivotal role in EG-501’s research and development by enabling target nomination and indication selection.
Addressing R&D Challenges
- Traditional drug development faces challenges such as lengthy target validation cycles and high clinical translation failure rates.
AI Platform Implementation in EG-501 Development
- Target nomination & indication:AI nominated neuroinflammation and NMDA receptor dysregulation as targets for NPSLE‑CI, and supported selecting NPSLE‑CI as the indication.
- Pathways & hypotheses:
AI integrates pathway analysis, links LPS-induced TLR4 activation to NMDA dysregulation, and predicts EG501’s rescue of PI3K-AKT persistence via KEGG enrichments in related models.
AI performs semantic analysis, nominates EG501 for chronic slowing, and identifies persistent PI3K-AKT as a key differentiator.
- The AI-driven approach demonstrates a scalable playbook, integrating KEGG enrichment, pathway analyses, and histological/behavioral outcomes to substantiate substantial improvement over no available therapies.
